
433MHz or 868MHz wireless alarm system, what's the difference?
Wire-free, easy to install, portable etc these are benefits to use wireless alarm system. Everyone knows wireless alarm system utilizes wireless frequency to communicate with each devices. Typically every countries have Radio Spectrum Regulatory Agencies (i.e. FCC in USA) which mainly responsible for management of radio spectrum.
433MHz and 868MHz bands belong to ISM
According to international radio spectrum regulations, the industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) bands are radio band reserved internationally for the use of radio frequency (RF) for industrial, scientific and medical purposes other than telecommunication. In recent years, ISM bands have also been shared with (non-ISM) license-free error-tolerant communications applications such as wireless alarm system. 433MHz, 868MHz are two major bands commonly used in wireless alarm system.
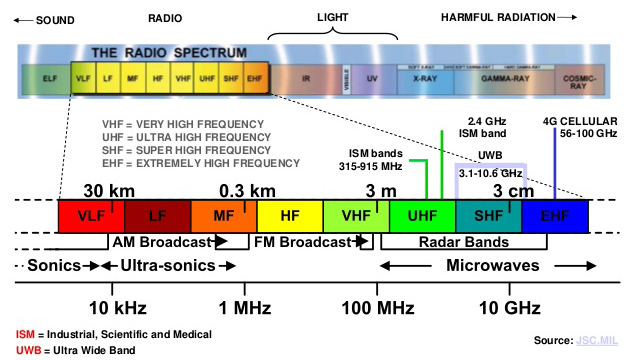
What's the difference between 433MHz and 868MHz?
As we mentioned above, both bands belong to free-license ISM bands. 433MHz frequency band has been widely used in almost many control applications, while 868MHz is exclusively reserved for communication between wireless sensor networks. Since many wireless products utilize 433MHz band, which can lead to interference/disturbance of communication between different products. 868MHz band is exclusively opened for wireless alarm system, it's less likely to be interfered.
433MHz and 868MHz, which is better?
In terms of transmission distance, generally, signals with longer wavelengths travel a greater distance and penetrate through, and around objects better than signals with shorter wavelengths. Higher frequencies result in shorter wavelengths. Technically 433 MHz can travel a greater distance than 868 MHz. But 433 MHz and 868 MHz may have the same radio frequency (RF) transmission performance, because there are many other factors determined this performance.
How is range determined?
Transmit power and receiver sensitivity are two factors determine range. dB - Decibels are logarithmic units that are used to measure RF power. Transmit power refers to the amount of RF power that comes out of the RF transmitter. Receive sensitivity refers to the minimum level signal the radio can demodulate. The higher transmit power or receiver sensitivity may result in greater transmission distance.
ASK and FSK, GMSK modulation
ASK - Frequency-shift keying: A type of amplitude modulation that assigns bit values to discrete amplitude levels. The carrier signal is then modulated among the members of a set of discrete values to transmit information.
FSK - Amplitude shift keying: A type of frequency modulation that assigns bit values to discrete frequency levels. FSK is divided into noncoherent and coherent forms. In noncoherent forms of FSK, the instantaneous frequency shifts between two discrete values termed the "mark" and "space" frequencies. In coherent forms of FSK, there is no phase discontinuity in the output signal. FSK modulation formats generate modulated waveforms that are strictly real values, and thus tend not to share common features with quadrature modulation schemes.
GFSK - Gaussian frequency-shift keying: A type of frequency shift keying modulation that uses a Gaussian filter to smooth positive/negative frequency deviations, which represent a binary 1 or 0. It is used by DECT, Bluetooth, Cypress WirelessUSB, Nordic Semiconductor, Texas Instruments LPRF, Z-Wave and Wavenis devices. For basic data rate Bluetooth the minimum deviation is 115 kHz.
Get My Latest Posts
Subscribe to get the latest updates.
Your email address will never be shared with any 3rd parties.
Tags: Alarm system